Robotic Surgery Training in Japan
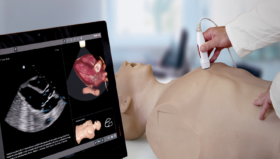
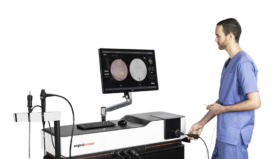
The RobotiX Mentor simulator provides prostatectomy experience and more.
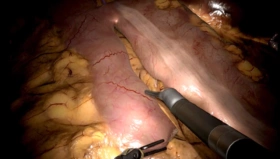
Matto Central Hospital in Hakusan, Japan was established in 1948, to provide regional medical services. The use of the new da Vinci robotic surgery equipment required hands-on training and experience.
The Challenge
Physicians required training on new robotic surgery techniques for prostatectomy and other skills and procedures.
“Since ours is a relatively small hospital, finding money in the budget for a simulation lab was difficult,” said Dr. Yuji Maeda (Chief of Urology). “However, the existence of the robotic skills lab was clearly attractive to the surgical residents.”
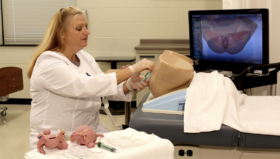
Skills mastery on the RobotiX Mentor is the foundation of robotic surgery training.

The Solution
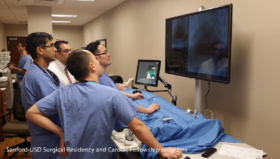
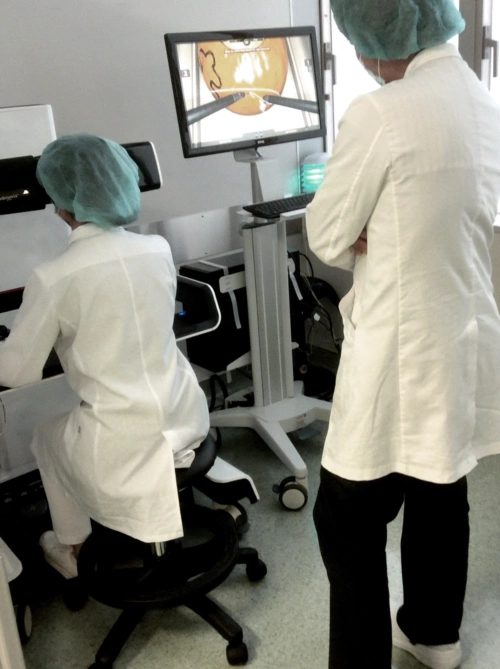
The hospital purchased a Robotix Mentor training simulator so that the physicians can learn robotic surgery. Now the program is being expanded to include residents.
“Surgical Science is the surgical simulator leader and the Robotix Mentor has advanced, highly life-like prostatectomy modules,” said Dr. Yuji Maeda. “It was very fortunate for us that we were introduced to the Robotix Mentor in Japan.”
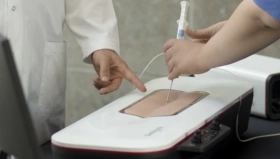
The robotic prostatectomy course is comprised of two parts: finishing Robotix Mentor prostatectomy modules, followed by using the dry box practice with the real da Vinci surgical system. Before the actual surgery, at least 20 hours of training is needed. The goal is to get comfortable handling the da Vinci surgical system. Free-hand procedural modules are used to practice surgeries before going into the OR.
“Physicians and residents like to use Robotix Mentor but the most frequent user in our hospital is the chief surgeon who performs 50 or more robotic prostatectomy cases per year,” said Dr. Maeda.
The Outcome
The RobotiX Mentor has generated considerable interest in robotic surgery and urology, as well as provided physicians and residents with the knowledge and skills needed prior to working with patients.